○ 본문요약 :
폴란드 바르샤바 대학교 (University of Warsaw ) 의 연구원 들은 DLW (Direct Laser Writing) 3D 인쇄 기술을 사용하여 마이크로 미터 크기의 렌즈를 설계했습니다. 3D 프린트 렌즈는 깨지기 쉬운 그래 핀 유사 재료를 포함하여 다양한 재료로 제작할 수 있습니다.
물리 학부에 기반을 둔 연구팀은 렌즈가 양자점이나 원자 적으로 얇은 2D 물질과 같은 단일 나노 미터 크기의 발광기의 분광 측정을 수행하는 데 필요한 부피가 큰 현미경 대물 렌즈를 대체 할 수 있다고 설명했다.
Researchers at the University of Warsaw, Poland, have designed micrometre-sized lenses using a Direct Laser Writing (DLW) 3D printing technique. The 3D printed lenses can be fabricated on top of various materials, including fragile graphene-like materials.
The research team, based in the Faculty of Physics, explains that the lenses can replace bulky microscope objectives that were previously required for performing spectroscopic measurements of single nanometre-sized light emitters, like quantum dots or atomically thin 2D materials.
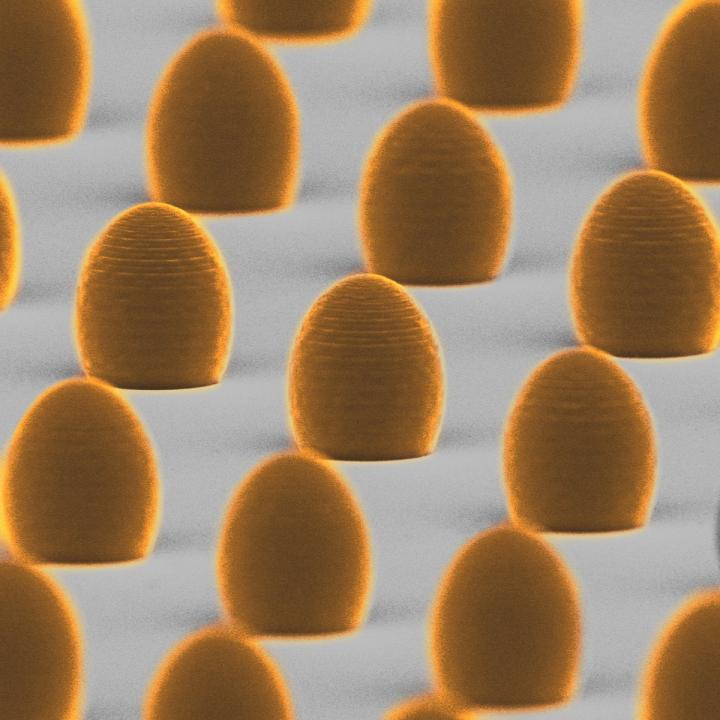
3D 프린팅 된 비구면 마이크로 렌즈의 주사 전자 현미경 이미지. 바르샤바 대학을 통한 사진.
3D 프린팅으로 마이크로 렌즈 제작
연구원들은 상업적으로 이용 가능한 3D 프린터가 빠른 개발을 경험하고 있으며, 이는 높은 광학 품질의 투명한 매체를 포함하여 호환 가능한 재료와 일치한다고 설명했습니다. 이러한 재료와 함께 3D 프린팅 기술의 발전은 생물학, 의학, 메타 물질 연구, 로봇 공학 및 마이크로 광학을 포함한 많은 과학 기술 분야에서 새로운 가능성을 열어줍니다.
Producing microlenses with 3D printing
The researchers set out by explaining that commercially available 3D printers have been experiencing rapid development, which has coincided with its compatible materials, including transparent media of high optical quality. The advancement of 3D printing technology alongside such materials opens up new possibilities in many fields of science and technology including biology, medicine, metamaterials studies, robotics, and micro-optics, the researchers state.
○ 출처 : 
https://bit.ly/3bDEFoZ
















