[해외]베이징 연구원, 저온 FDM 용 항균 필라멘트 개발
- 2020-04-29
- 관리자
○ 본문요약 :
연구원 화학 기술의 베이징 대학은 전분 풍의 폴리 카프로 락톤 (PCL)이 저온 FDM 기계를 사용하기 위해 합성 필라멘트 기반 개발했습니다. 생물 활성 성분의 첨가를 통해 필라멘트를 추가로 관능 화시켜 항균 특성을 제공 하였다.
Researchers from the Beijing University of Chemical Technology have developed a starch-infused polycaprolactone (PCL)-based composite filament for use with low-temperature FDM machines.
PCL보다 더 큰 물리적 특성을 가진 새로운 복합 필라멘트를 성공적으로 만든 후 팀은 기능으로 전환했습니다. 연구진은 복합 필라멘트 믹스 에 두 가지 유기 항균제 인 암모늄 -73과 PHMB를 첨가했습니다.
After successfully creating a novel composite filament with physical properties greater than that of PCL, the team turned to functionality. They wanted to go above and beyond, so they added two organic antibacterial agents, ammonium-73 and PHMB, to the composite filament mixes.
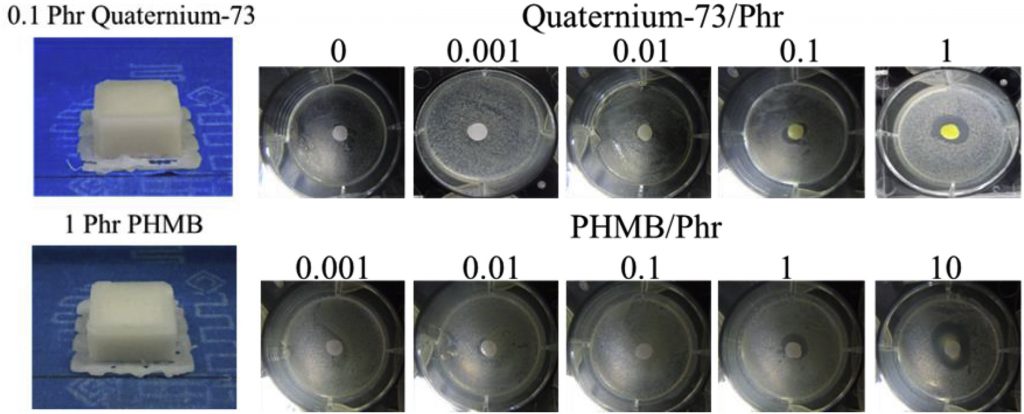
항균 샘플의 억제 구역. BUCT를 통한 이미지.
다양한 유기 제 농도를 갖는 항균 샘플을 복합 필라멘트를 사용하여 3D 인쇄하고,이. 콜라이 및 에스. 아우 레 우스의 배양 물을 갖는 페트리 접시에 넣었다. 예상 한 바와 같이, 페트리 디쉬 (제로 박테리아 성장 영역)의 억제 구역은 더 높은 농도의 항균제로 넓어졌다. 필라멘트의 인쇄 온도가 낮기 때문에, 유기 제는 변성되지 않고 인쇄 공정 내내 활성을 유지 하였다. 이 결과는 항균 특성을 갖는 저온 복합 필라멘트의 제조 및 기능화 방법을 검증했다.
Antibacterial samples with various organic agent concentrations were 3D printed using the composite filament, and placed in petri dishes with cultures of E. coli and S. aureus. As expected, the inhibition zones of the petri dishes (the areas of zero bacterial growth) broadened with higher concentrations of antibacterial agents. Due to the low printing temperature of the filament, the organic agents did not denature and remained active throughout the printing process. This result validated the researchers’ method of producing and functionalizing low-temperature composite filaments with antibacterial properties.
○ 출처 : 
















